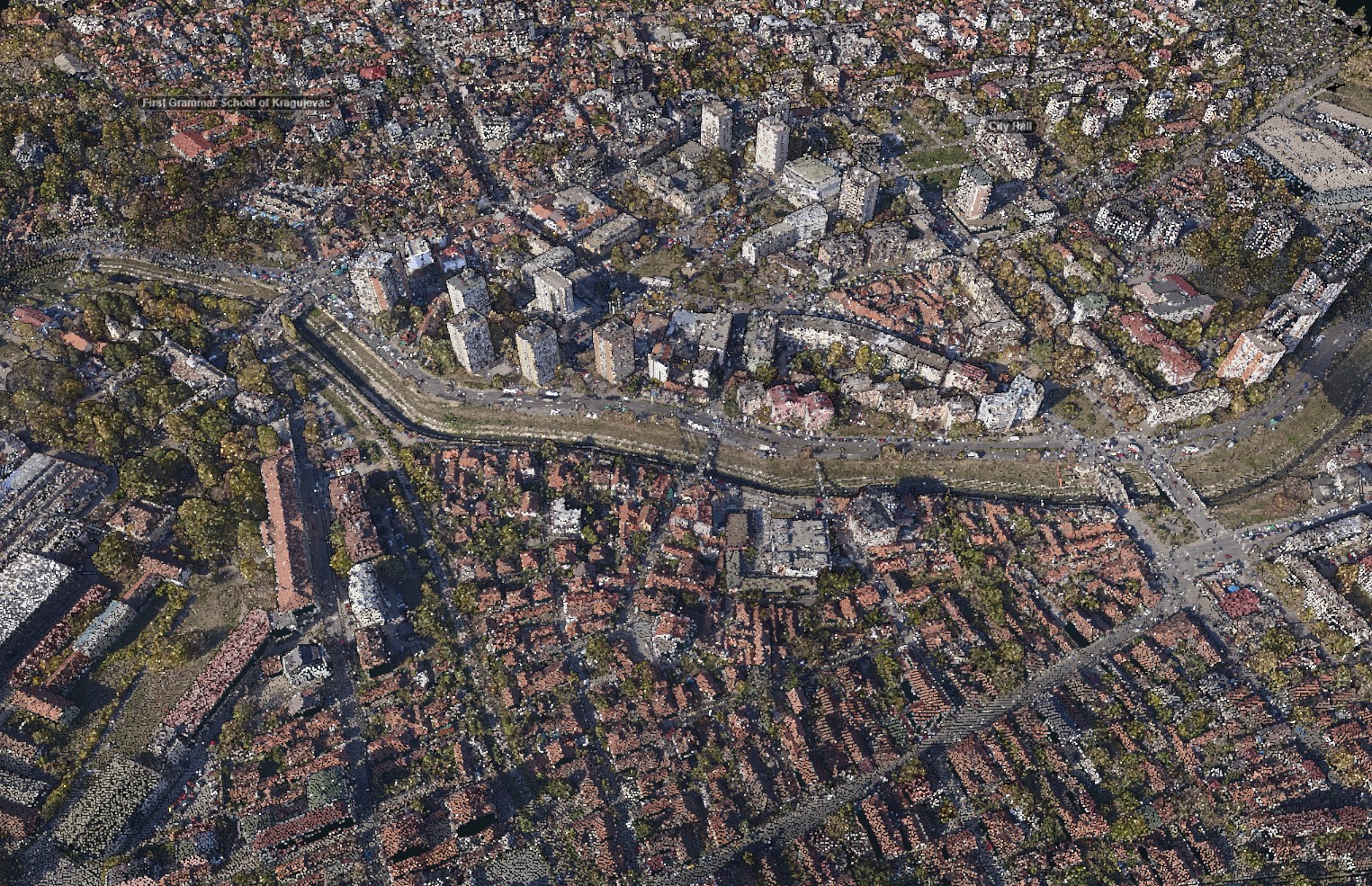
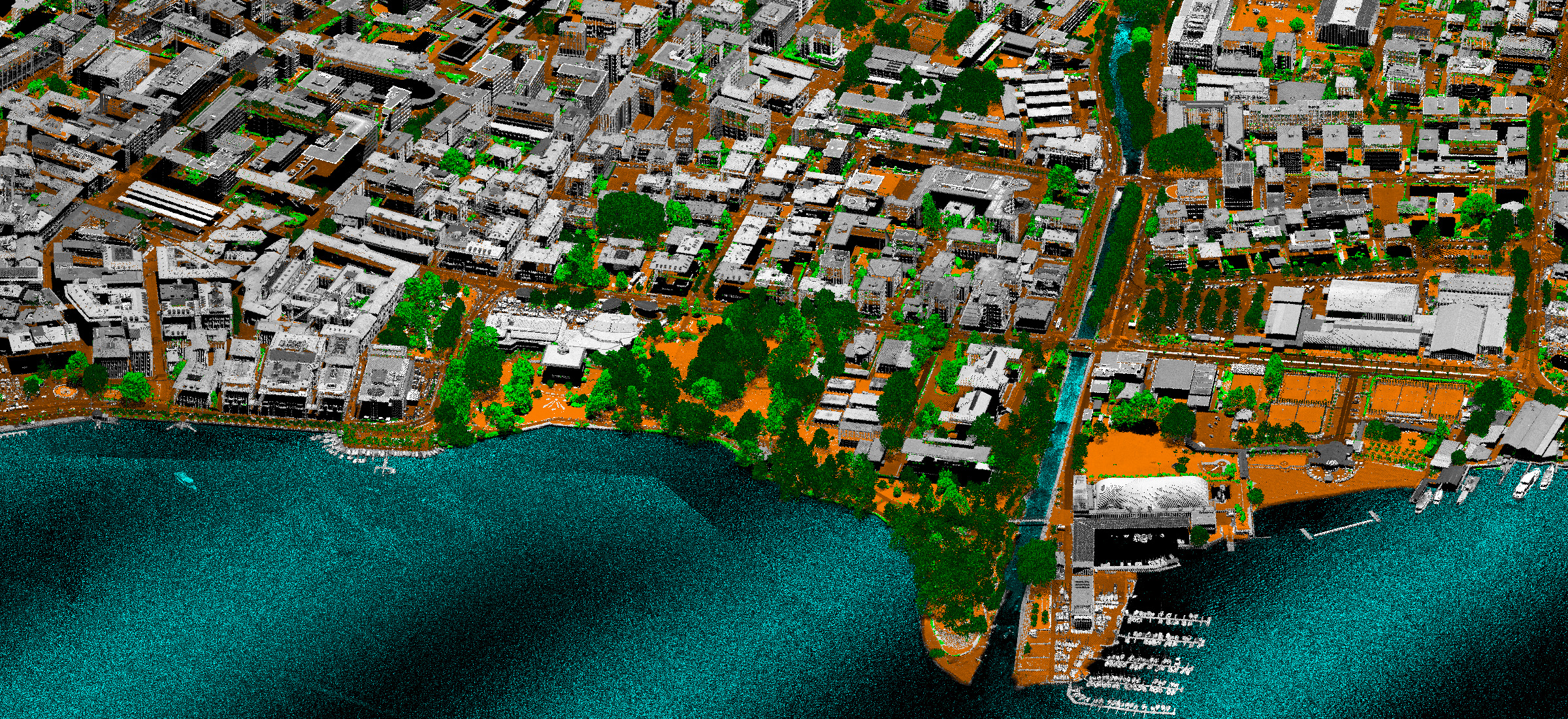
Point cloud
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is method of remote sensing which uses light in the form of laser pulses to measure the distance to the surface. Once emitted light beam reflects from the surface, the sensor measures the time and the amount of reflected light and thus determine the distance to the object / surface. The data from LIDAR, combined with other data collected by photogrammetry, provide precise, three-dimensional information about the spatial entities and their characteristics, whether they are natural (surface terrain, vegetation) or artificial (buildings).
In addition to imaging with RGB+NIR camera, MapSoft offers data collection by LiDAR system. In fact, the best possible interpretation of the collected spatial data is obtained by the simultaneous imaging with aerial camera and LiDAR, which is the way MapSoft is working. In this way, high accuracy spatial data are collected: three-dimensional coordinates of each point comes from LiDAR's point cloud and color from aerial images made by high quality aerial metric camera.
Each point in the cloud is assigned a class attribute through the classification process. Classification can be done:
- by automatic methods (very fast procedure, few days after flight mission) or
- manually, by checking and correction of previously automatically classified point cloud (the highest level of accuracy and confidence).
Specification
- Point cloud in LAS, LAZ, PLY format
- Colorization from georeferenced images not from the orthophoto
- Density up to 100 points/m2
- Four channels (RGB+NIR)
- Accuracy up to 3-10 cm (depending on flying altitude)
- Up to 8 returns from single laser pulse
Applications
- Hydrology
- Forestry
- Infrastructure design
- Power lines design and vegetation management
- 3D visualization
- Archeology