Digital terrain model
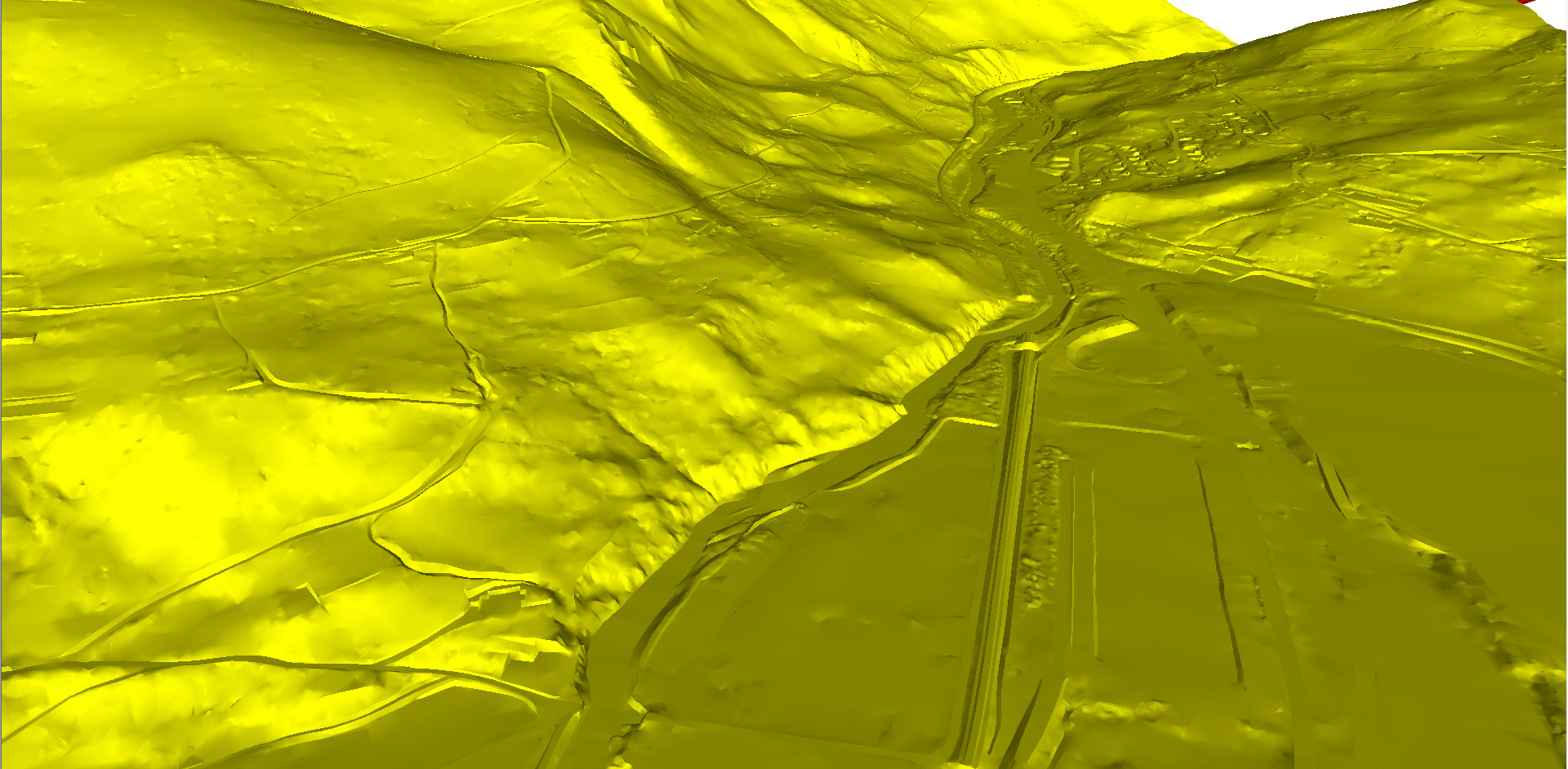
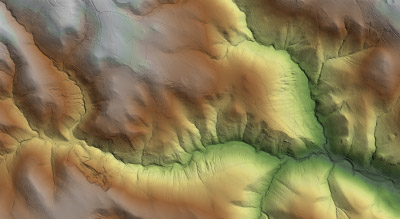
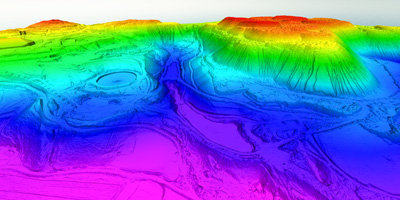
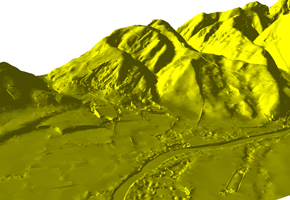
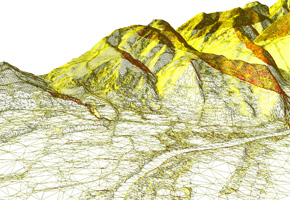
Digital terrain model (DTM) is standard way to represent the surface of the field in digital form. Surface of the field is represented by a mathematical model which is based on the use of proper height network (grid) or the use of a network of irregular triangles (TIN). These models are formed based on the known positions and heights of characteristic points and lines (structural and breaklines) of the ground.
Laser scanning (LiDAR) is the most effective method for DTM data collection. Laser scanning by high quality LiDAR scanner (Teledyne Optech Galaxy) and aerial imaging data collecting by metric camera (Phase One iXu RS1000) and subsequent data processing provide an optimal balance between demands for data quality, on the one hand and efficiency and economy on the other.
There are different processing levels and processing speed depending on the required accuracy:
- automatically classified cloud points - extracted ground points
- thinned ground points by height tolerance (automatic procedures - very fast)
- manually edited ground points + breaklines from aerial images (highest accuracy and reliability).
Specification
- Source data (points, lines, polygons) in standard vector formats (DXF, shape files, GML,…)
- Generated DTM in TIN or grid formats
- TIN in any standard vector formats (DXF, shape files, GML,…)
- Grid in any standard raster formats (GeoTIF,…)
- DTM accuracy up to 5 cm
- Contour lines generation
- Longitudinal and cross sections
Applications
- Hydrology
- Infrastructure design
- 3D visualization
- Visibility studies